Three smart cities in traffic management: Perth, Moscow, Mexico City
What makes a city truly smart is its traffic management operations…
In this two-part feature Intertraffic spoke to the cities that we believe are indeed the smartest in the world from a traffic management perspective and asked their representatives just what it is that makes their cities so smart. Starting with examples from Perth, Moscow and Mexico City.
1.Route Managers in Perth, Western Australia
2.MaaS, V2I and more in Moscow
3.Traffic Control in Mexico City
But what is in fact smart? Enter the search term “smartest city in the world” into Google and two things are a certainty. One, there’ll be more than 20m results and two, you will be told that it’s Singapore. Or London. Or Zurich. Or Copenhagen. However, expert opinion will tell you that these essentially arbitrary lists have no real meaning unless we define what is meant by “smartest”.If by smartest we mean “most intelligent traffic management operations” then you won’t necessarily find such a list in a search engine, however Amsterdam and Los Angeles have both made headline news this year with their ambitious traffic management plans. To obtain such a list one has to canvass the aforementioned expert opinion and combine it with extensive research and industry knowledge before compiling the world’s six smartest cities from a traffic management perspective, while also taking into consideration the fact that the citizens of and visitors to those cities are probably only aware of just how smart they are when something goes wrong. Otherwise the city’s smartness is imperceptible to the human eye.
1.Traffic management in Perth, Western Australia
Tony Earl, Executive Director Road Network Operations · Main Roads Western Australia
“What makes Perth the Smartest City in Australia in terms of traffic management? It’s the strategy and subsequent journey in response to the 2015 Auditor General’s report into Main Roads WA Management of congestion:
1. Get the right people in place
2. Measure performance and set targets
3. Optimise the performance of the Arterial Road and Freeway networks
4. Select the right projects.
This “smart” strategy led to targeted recruitment of a leadership team with World City experience and a track record in congestion management to take Main Roads on a capability development journey.”
At the heart of the new capability is the development of a world class brand-new state of the art multi-functional, multi-skilled Road Network Operations Centre (RNOC).

Traffic control centres from mining remote operation centres
“The RNOC facility would not look out of place at NASA, but the design is in fact a hybrid of best in class traffic control centres and importantly the learnings we have taken from the two remote mining operations centres here in Perth: BHP and Rio Tinto, both very advanced in the automated and connected environment.”
“A particular focus in those environments is the efficient and continuous operation of the supply chain to rapidly remediate any breakdown or efficiency drop off in mining production and we have adopted this philosophy in the RNOC for the operation and productivity of the State Road Network.”
“The experience we gained from these mining company operations centres significantly highlighted the value of developing pervasive road network situational awareness and a common operating picture for all of the staff throughout the 2000m2 facility, through dashboard development to easily consume smart data.”
“The RNOC brings together all the component parts of a world class Smart Network Operator to manage traffic in an open plan, collaborative and high tech environment. All of these areas have had a significant capability uplift and continuous development with staff trained by experts in their field, but it is how they operate as a single seamless entity which really makes Perth’s Traffic Management operation smart. Real Time Operations, Planned Interventions, SCATS traffic signal optimisation, Data Analysts, Operational traffic Modellers, Traffic Management Services, Congestion Project Managers and Intelligent Transport Systems. In addition, and fundamental to the RNOC operating model, Route Managers are a vital new concept we developed.”
“In the main, our current seven Route Managers have completed Main Roads’ three year Graduate Civil Engineering Program and then undertaken an RNOC specific bespoke additional 18-month programme in all of the above skill sets to understand all aspects of what makes a World class Smart Network Operator. These staff who were at the start of their careers are now highly capable Route Managers accountable for mobilising RNOC resources for planning and operations of their assigned routes under the guidance of experienced Area Managers. This operating model, together with targeted investments as a result of smarter data analytics has yielded year on year reductions in the cost of congestion on the Perth State Road network.”
“Key to this success has been the ability to measure performance indicators and present multi-dimensional analysis of the 29 State Routes to support targeted operations and investment. Through the development of control and data systems combined with ITS device deployment, we can now measure in forensic detail the cost of congestion and a multitude of other performance indicators which enables our data analytics team and operational modellers to accurately predict potential benefits in a change of operational strategy of our traffic signals or other assets or physical low cost investment options and present information in a way that is visually intuitive, even to lay stakeholder’s, including politicians - that’s smart!”

Kwinana Northbound Smart Freeway
This was demonstrated by the implementation of Australia’s most advanced and Western Australia’s first major ITS project, Kwinana Northbound Smart Freeway, which recently celebrated its first year of very successful operation. The implementation of this initiative effectively delivered an upgrade to this physically constrained section of the freeway to provide more reliable journeys, a safer driving experience and reduced congestion.
“Our Route Managers working with our smart analysts and operational modelling people predicted up to 10 minutes journey time saving and on the first day of operations, this was achieved, with a current average saving during the AM peak of five minutes whist increasing the “productivity” of the Freeway by 13% in terms of traffic throughput at the Narrows bridge.”
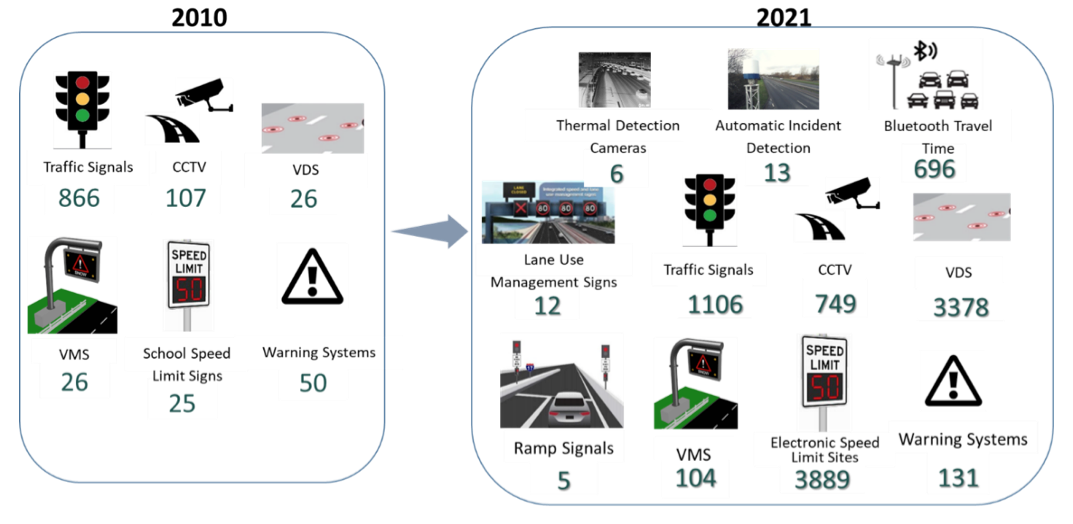
“In Perth, roadside technology and control system upgrades are now being delivered as part of numerous road and ITS projects, which are becoming more and more common as we focus on making best use of existing infrastructure. Our smart infrastructure has increased significantly over the past 10 years but exponentially over the last three years with a number of newly adopted technologies implemented on our first Smart Freeway for congestion management, electronic Lane Use Management signs, Coordinated Ramps Signals and in a first for Australia, Radar based stopped vehicle incident detection.”
“Due to the success of the first, we are currently working on our second and much larger Smart Freeway; Mitchell Freeway Southbound, which will be a considerable challenge to incorporate 16 new ramp signals to manage the phenomenon of flow breakdown, utilising complex smart algorithms.
A snapshot of just some of the increases in technology on our road network over the past 10 years is presented below.”
“In Perth, we are continually developing our smart systems and smart people in order to turn information into intelligence, into informed decision making to support our vision; Perfect Predictable journeys, 24/7.”
2.Traffic management in Moscow
The number of cars constantly increases in Moscow. According to the data from the State Automobile Inspectorate, by the end of 2020 in the Moscow metropolitan area there were 8.4 million cars registered, which is 170,000 vehicles more than in 2019. We spoke to Olga Smirnova, International Relations Coordinator, Department of Transport and Road Infrastructure Development, Moscow.
“Nowadays the Moscow Traffic Control Centre is a powerful technological centre, which applies cutting-edge information technologies for traffic management. Since 2011 an Intelligent Transport System has been developed so for a decade we have had a chance not only to observe traffic flow in real time, but also to forecast the traffic situation, regulate transport flows, monitor important transport infrastructure objects. Now we operate a system that controls more than 40,000 traffic lights, 185 information screens, more than 3000 photo- and video-cameras for tracking road rules violation and 3900 sensors. We make sure that the whole system works 24/7.”
Internet of Things
“With the development of the Internet of Things and computer modelling it has become possible to create a digital model of any physical object – now a digital twin of Moscow is being developed. A digital twin is a prototype of a real city, upon which it is possible to analyse the real situation on the roads, the response to possible changes and external input. It is an accurate reflection of the city in the digital realm, information to which comes from different sensors, monitoring systems and resource counters.”
“A dynamic transport model is already operating in Moscow, allowing us to evaluate the road traffic situation in real time, make short-term forecasts and inform residents 24/7. Muscovites receive targeted SMS and push-notifications on their smartphones about changes in public transport operation and traffic situation. The information distribution is built upon transport behaviour, profile and situational triggers of a particular person. Nowadays more than 4.5 million Moscow residents receive the information.”
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure V2I
“One of the most ambitious projects with the aim of raising road safety levels is the development and implementation of a vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication system. V2I is a system of wireless connection allowing vehicles to share data with traffic lights and road signs, for example, using incorporated sensors and detecting devices. In the near future piloting of the technology will start in Moscow. It is an integral part of autonomous vehicles development. We expect that its launch in Moscow will increase road safety, as the human factor will be reduced to a minimum.”
Mobility as a Service for multimodal transport
“All online transport and traffic management services of Moscow gravitate towards mutual integration so that users feel comfortable using it. To solve the task Moscow has embraced the concept of Mobility as a Service (Maas). We have united all the transport services in the Moscow Transport app for the users to build multimodal routes, hire taxis, book car-sharing, learn about the arrival of buses and trams in real time and check the loading of public transport. The app is already translated into 6 languages. By the end of 2021 we will start gradually increasing its features with services that allow planning trips with different modes of public transport with predetermined or dynamic cost. There it will also be possible to pay for the trip.”
The Moscow Transport app won Best MaaS Initiative at the International Transport Ticketing Award 2021. The updated app will be presented at Intertraffic Amsterdam 2022.
“For the past 10 years we have re-organised traffic flow on 80% of the road and street network in Moscow.”
Vision Zero
“Moscow adheres to the international Vision Zero concept, which helps to set up measures to increase transportation safety. Based on this concept, safe road and transport infrastructure is planned. For the past 10 years we have re-organised traffic flow on 80% of the road and street network in Moscow.”
“Implementation of photo- and video-recording of violations in accident spots reduced road accidents by 30%. Apart from the major feature, the cameras serve as detectors for counting the number of vehicles (analysis of highway load) and are used to search for stolen vehicles. On average, each car is registered on 14 cameras every day. The processing of materials from cameras takes place in several stages. The neural network automatically verifies the brand and license plate of cars for their compliance with the database. If the car is on the wanted list, the system assigns the corresponding sign of each fixation with it. The data is available for use by law enforcement officers, in addition, it is possible to receive data online for instant response and detention of these vehicles. Due to the possibility of using data from the cameras, the number of stolen cars has decreased each year, from 13,000 in 2012 to just 1500 in 2019. One of the main tasks remains the implementation of innovative methods of traffic management that meet the growing demands of mobility of Muscovites and visitors to the capital.”
3.Traffic management in Mexico City
When talking about mega-cities, that is, urban conglomerates that exceed 10 million inhabitants, large super-populated capitals appear, such as Guangzhou, Tokyo, Shanghai or New York. The 2010 census for Mexico City, showed a population of 9.2 million inhabitants, but its daily dynamics, in terms of statistics related to movement, would suggest that this is a huge underestimation. We spoke to José C Azcárate, General Directorate of Traffic Engineering, Mexico City.
“The Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico (ZMVM) is made up of 16 districts of Mexico City, but to this population are added 60 suburban municipalities of the states of Mexico and Hidalgo. In this way, the population that interacts in the same urban area, reaches population figures that exceed 21.8 million people.”
“The concepts of Smart City and Smart Mobility are terms that are not very well defined in Mexico City, nor are they for most cities in Latin America. Even so, without great state-of-the-art technological support, we must move forward with the mobility of this pandemonium. Every day, at all hours.”
Control & responsibility
“The public administration of Mexico City places the responsibility of coordinating a number of daily trips that, according to official figures, would reach 25 million trips per day (but we assume that this number is much higher), on a department called “Undersecretary of Traffic Control”, who, contrary to what might be expected, does not depend on the city's Ministry of Mobility, but on the Ministry of Citizen Security.”
“Let's continue a bit with the complex statistic of this city. The vast majority of commutes made in the ZMVM are assumed by concessioned public transport (80%), made up of independent carriers subrogated to routes stipulated and regulated by the administration. The vast majority of them grouped in coalitions, alliances, cooperatives and unions, but they are a minority that are constituted in formal companies. This modality is called Man-Bus, because practically each owner is the driver of the unit.”
The type of vehicle that offers this service are minibuses, midibuses, buses and vanettes, although the largest volume is made up of minibuses and vanettes. The pseudo-official figures for the number of commutes made in this modality is 11.54 million, but adding joint operations of the ZMVM, it is assumed that the real number is substantially higher. The number of vehicles in this modality reaches 200,000 only in those registered in Mexico City.
The rest of the transport offer is distributed as follows (million trips per day):
• Collective Transportation System (SUBWAY) 4.47
• Taxis + Application Vehicles (Uber, Cabify, etc.) 1.64
• BRT Systems (Metrobús/Mexibús) 1.11
• Suburban Buses (Private in Concession) 0.91
• Urban Buses (RTP/M1/ Trolleybus) 0.41
• Others (Cablebus, Scooters, Bicycles) 0.54
• Mototaxis/Suburban service 0.27
To these modalities, we should add the population of 4.8 million private cars registered only in Mexico City. According to figures from the Ministry of Mobility, people who use collective public transport spend approximately 54% more time in their transfers than those who do it in their own car.
“Returning to "the brave" who are in charge of coordinating the concert of millions and millions of people attending and crowding the communication arteries of this troubled city. Let's take a look at how they try to manage traffic flows. We will begin by stating that the arm acting on the roads is made up of a fleet of more than 1,800 control vehicles (patrols) that are operational.”
Traffic light control
“Traffic light control in Mexico City is based on a system that has been growing and improving gradually over time. The growth is evident in the location of concentric groups that little by little have been incorporating self-adaptive systems in their conformation.”
“Traffic light control in Mexico City is based on a system that has been growing and improving gradually over time”
“Another invaluable support in monitoring traffic behavior is the Center for Emergency Attention and Citizen Protection (C5). Let us remember that the Traffic Control body belongs to the Ministry of Citizen Security, so the support of this C5 is naturally integrated.”
“The C5 operates with more than 15,000 cameras (PTZ the largest number of these), in conjunction with 911 systems, one on normal phone lines and one on IOS and Android applications. There are 138 devices for speed control (Photo-Civics) in the metropolitan area.”
“A final observation should be made about the traffic regulator in the ZMVM. It operates with a limited budget, which does not imply that the results should be limited too. The city must move, always, at all times, with little ‘Smart’ but a lot of ‘Mobility’.”
We will follow up on three other cities in another episode of this article. Stay tuned via our newsletter >
Share your story
Do you have an innovation, research results or an other interesting topic you would like to share with the professionals in the infrastructure, traffic management, safety, smart mobility and parking industry? The Intertraffic website and social media channels are a great platform to showcase your stories!
Please contact our Sr Brand Marketing Manager Carola Jansen-Young.
Are you an Intertraffic exhibitor?
Make sure you add your latest press releases to your Company Profile in the Exhibitor Portal for free exposure.





